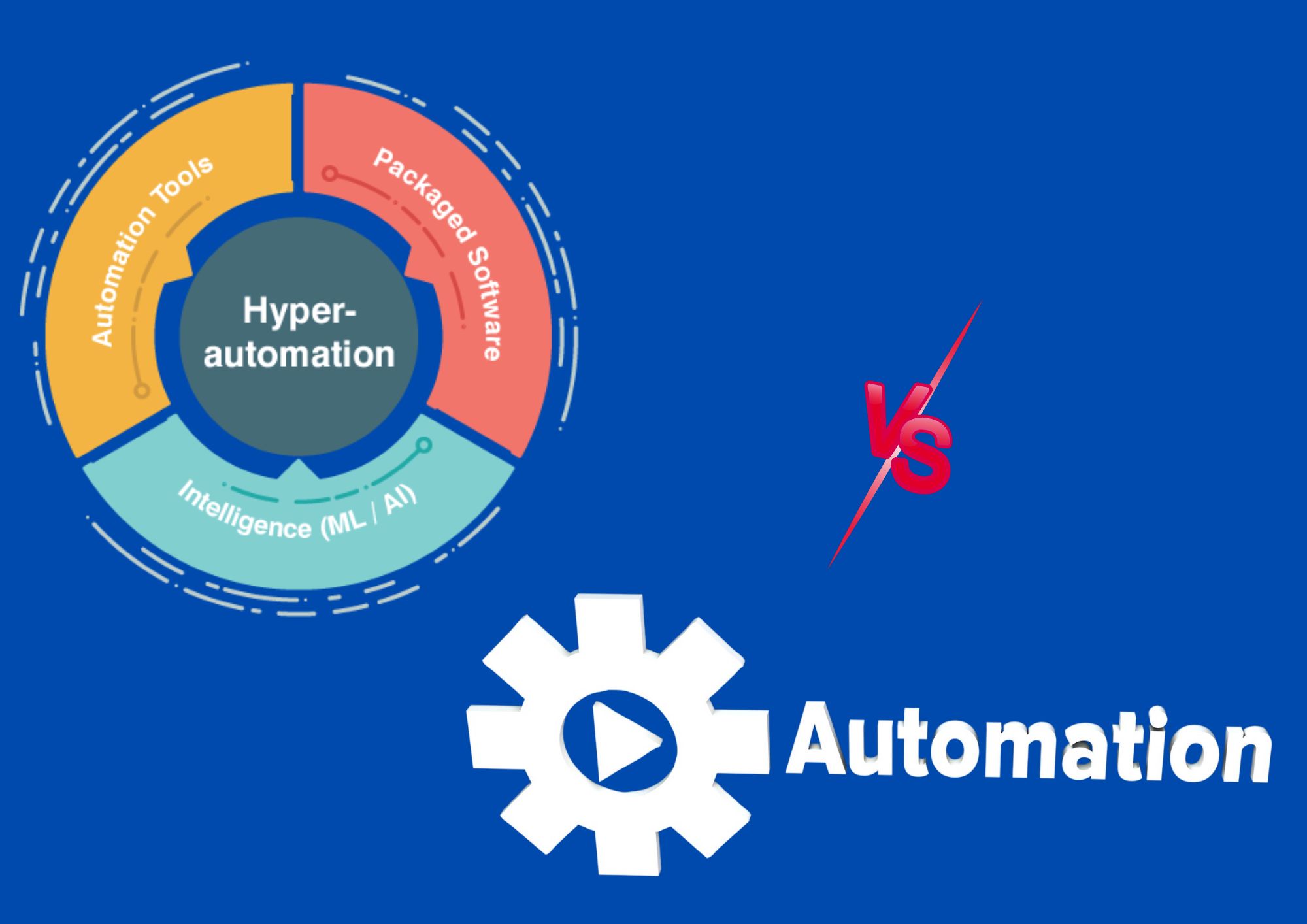
Hyper automation and traditional automation have been making headlines in recent years as companies look for ways to streamline processes, improve efficiency, and reduce costs.
However, understanding the differences between these two approaches can be challenging, especially when you’re trying to decide which one is right for your business.
In this article, we’ll explore the key differences between hyper automation and traditional automation, providing you with real-life examples, facts, and figures to help you make informed decisions for your organization.
Section 1: Understanding Traditional Automation
Traditional automation has been the go-to solution for businesses looking to automate routine tasks, streamline processes, and increase productivity.
It involves using technology to perform tasks that would otherwise require human intervention, such as data entry, inventory management, and basic customer service interactions.
1.1 Advantages of Traditional Automation
- Improved efficiency: Automation can help reduce human error, cut down on manual labor, and speed up processes.
- Cost savings: Automating repetitive tasks can lead to a reduction in labor costs over time.
- Scalability: Traditional automation solutions can be scaled up to handle larger volumes of work as your business grows.
1.2 Limitations of Traditional Automation
- Lack of flexibility: Traditional automation solutions often rely on fixed rules and workflows, making it difficult to adapt to changes in business requirements.
- Limited scope: Traditional automation can only handle specific tasks, leaving more complex tasks to be performed by humans.
- Integration challenges: Implementing traditional automation can be challenging if it needs to integrate with multiple systems or software platforms.
Section 2: The Emergence of Hyper Automation
Hyper automation is a more advanced approach to automation that combines artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and other advanced technologies to create highly adaptable, flexible, and scalable automation solutions.
2.1 Key Components of Hyper Automation
- AI and ML: These technologies enable hyper automation to learn, adapt, and improve over time, making it more effective at handling complex tasks and changing business requirements.
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA): RPA uses software robots to perform repetitive tasks more efficiently than humans, freeing up employees to focus on more strategic work.
- Process mining: This technique analyzes data from various sources to identify inefficiencies and areas for automation, helping businesses optimize their processes.
2.2 Advantages of Hyper Automation
- Enhanced flexibility: Hyper automation can adapt to changes in business requirements and handle more complex tasks than traditional automation solutions.
- Improved decision-making: AI and ML-powered hyper automation can analyze large volumes of data to provide valuable insights, helping businesses make more informed decisions.
- Greater ROI: By automating a wider range of tasks and improving overall efficiency, hyper automation can deliver greater long-term cost savings than traditional automation.
Section 3: Hyper Automation vs. Traditional Automation: A Side-by-Side Comparison
To better understand the differences between hyper automation and traditional automation, let’s compare their key features, benefits, and limitations.
3.1 Flexibility and Adaptability
Hyper automation is more flexible and adaptable than traditional automation, thanks to its AI and ML capabilities.
For example, an AI-powered chatbot can understand and respond to a wider range of customer queries than a rule-based chatbot, providing a more personalized and efficient customer service experience.
3.2 Scope and Complexity
While traditional automation is limited to handling specific, repetitive tasks, hyper automation can tackle a broader range of tasks, including those that require complex decision-making or pattern recognition.
For instance, hyper automation can be used to analyze customer behavior patterns and create personalized marketing campaigns, whereas traditional automation would struggle to perform such tasks effectively.
3.3 Integration and Scalability
Hyper automation is designed to integrate seamlessly with various systems and platforms, making it easier to implement and scale up as your business grows.
On the other hand, traditional automation might require more time and effort to integrate with different systems, which can limit its scalability.
3.4 ROI and Cost Savings
While both hyper automation and traditional automation can lead to cost savings, hyper automation tends to deliver a greater ROI over time due to its ability to handle more complex tasks, adapt to changing business requirements, and optimize processes more effectively.
| Feature | Hyper Automation | Traditional Automation |
| Flexibility & Adaptability | High: AI and ML enable adaptability and handling of complex tasks. | Low: Fixed rules and workflows limit adaptability. |
| Scope & Complexity | Broad: Can handle complex tasks, pattern recognition, and decision-making. | Narrow: Limited to specific, repetitive tasks. |
| Integration & Scalability | Seamless: Easy integration with various systems and platforms. Scalable. | Challenging: Integration with different systems can be difficult. Limited scalability. |
| ROI & Cost Savings | Greater ROI: Handles complex tasks, adapts to changes, and optimizes processes. | Lower ROI: Limited to specific tasks, less adaptive. |
| Technologies Used | AI, ML, RPA, process mining, big data analytics, etc. | Rule-based systems, barcode scanning, etc. |
| Real-Life Application Example | Fraud detection in the financial industry. | Inventory management in the retail sector. |
Section 4: Real-Life Examples of Hyper Automation and Traditional Automation
To further illustrate the differences between hyper automation and traditional automation, let’s look at some real-life examples:
4.1 Hyper Automation Example: Fraud Detection
In the financial industry, hyper automation has been used to detect and prevent fraud more effectively than traditional automation methods.
By combining AI, ML, and big data analytics, hyper automation can analyze large volumes of transaction data in real-time, identify unusual patterns, and flag potential fraudulent activity for further investigation.
4.2 Traditional Automation Example: Inventory Management
In the retail sector, traditional automation has been used for years to streamline inventory management processes.
Barcode scanning technology and automated inventory management systems can track stock levels, reorder products when necessary, and reduce the risk of human error in the inventory management process.
In conclusion, both hyper automation and traditional automation offer significant benefits for businesses looking to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and streamline processes.
However, hyper automation, with its advanced AI and ML capabilities, offers greater flexibility, adaptability, and scalability, making it a more powerful solution for businesses facing complex challenges and rapidly changing market conditions.
By understanding the differences between hyper automation and traditional automation, you can make more informed decisions about which approach is best suited for your organization’s needs.
Whether you choose to adopt hyper automation, traditional automation, or a combination of both, the key is to leverage the power of these technologies to drive innovation, efficiency, and growth in your business.
Thank you for reading our blog, we hope you found the information provided helpful and informative. We invite you to follow and share this blog with your colleagues and friends if you found it useful.
Share your thoughts and ideas in the comments below. To get in touch with us, please send an email to dataspaceconsulting@gmail.com or contactus@dataspacein.com.
You can also visit our website – DataspaceAI